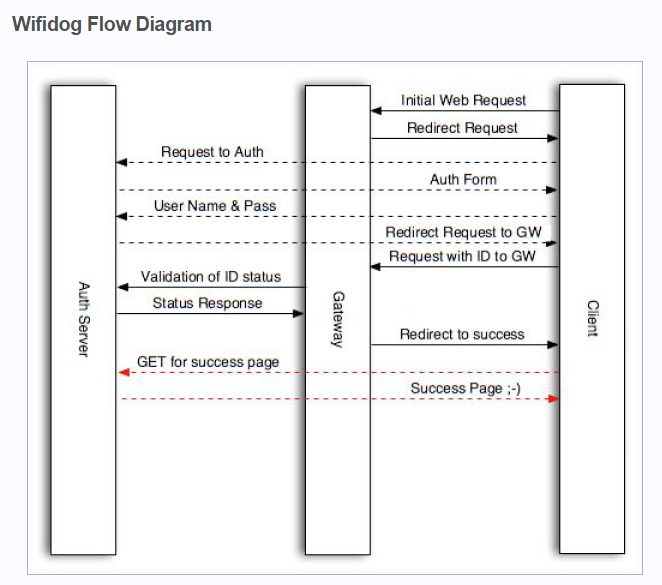
wifidog用php实现验证流程
步骤
1.首先简单说说wifidog认证的过程
客户端首次连接到wifi后,浏览器请求将会被重定向到:
login/?gw_address=%s&gw_port=%d&gw_id=%s&url=%s
验证通过后,客户端被重定向到网关,url格式如下:
http://网关地址:网关端口/wifidog/auth?token=
wifidong会启动一个线程周期性地报告每一个用户的状态信息,并通过如下地址发送给认证
服务器:
auth_server:/auth/?stage=
ip=
mac=
token=
incoming=
outgoing=
认证服务器根据该状态信息决定是否允许该用户继续连接,并回复网关,回复格式为:Auth:状态码,
如:Auth:1
常用状态码:
0:AUTH_DENIED,表示拒绝
1:AUTH_ALLOWED,验证通过
验证通过后,将重定向到如下地址:
portal/?gw_id=%s
wifidog的ping协议
wifidog通过ping协议将当前状态信息发送给认证服务器,发送地址为:
http://auth_sever/ping/?
gw_id=%s
sys_uptime=%lu
sys_memfree=%u
sys_load=%.2f
wifidog_uptime=%lu
认证服务器须返回一个“Pong”作为回应。
具体php实现代码如下
public function auth()
{
//响应客户端的定时认证,可在此处做各种统计、计费等等
/*
wifidog 会通过这个接口传递连接客户端的信息,然后根据返回,对客户端做开通、断开等处理,具体返回值可以看wifidog的文档
wifidog主要提交如下参数
1.ip
2. mac
3. token(login页面下发的token)
4.incoming 下载流量
5.outgoing 上传流量
6.stage 认证阶段,就两种 login 和 counters
*/
$stage = $_GET['stage'] == 'counters'?'counters':'login';
if($stage == 'login')
{
//XXXX跳过login 阶段的处理XXXX不能随便跳过的
//默认返回 允许
echo "Auth: 1";
}
else if($stage == 'counters')
{
//做一个简单的流量判断验证,下载流量超值时,返回下线通知,否则保持在线
if(!empty($_GET['incoming']) and $_GET['incoming'] > 10000000)
{
echo "Auth: 0";
}else{
echo "Auth: 1\n";
}
}
else
echo "Auth: 0"; //其他情况都返回拒绝
/*
返回值:主要有这两种就够了
0 - 拒绝
1 - 放行
官方文档如下
0 - AUTH_DENIED - User firewall users are deleted and the user removed.
6 - AUTH_VALIDATION_FAILED - User email validation timeout has occured and user/firewall is deleted(用户邮件验证超时,防火墙关闭该用户)
1 - AUTH_ALLOWED - User was valid, add firewall rules if not present
5 - AUTH_VALIDATION - Permit user access to email to get validation email under default rules (用户邮件验证时,向用户开放email)
-1 - AUTH_ERROR - An error occurred during the validation process
*/
}
public function portal()
{
/*
wifidog 带过来的参数 如下
1. gw_id
*/
//重定到指定网站 或者 显示splash广告页面
redirect('http://www.baidu.com', 'location', 302);
}
public function ping()
{
//url请求 "gw_id=$gw_id&sys_uptime=$sys_uptime&sys_memfree=$sys_memfree&sys_load=$sys_load&wifidog_uptime=$wifidog_uptime";
//log_message($this->config->item('MY_log_threshold'), __CLASS__.':'.__FUNCTION__.':'.debug_printarray($_GET));
//判断各种参数是否为空
if( !(isset($_GET['gw_id']) and isset($_GET['sys_uptime']) and isset($_GET['sys_memfree']) and isset($_GET['sys_load']) and isset($_GET['wifidog_uptime']) ) )
{
echo '{"error":"2"}';
return;
}
//添加心跳日志处理功能
/*
此处可获取 wififog提供的 如下参数
1.gw_id 来自wifidog 配置文件中,用来区分不同的路由设备
2.sys_uptime 路由器的系统启动时间
3.sys_memfree 系统内存使用百分比
4.wifidog_uptime wifidog持续运行时间(这个数据经常会有问题)
*/
//返回值
echo 'Pong';
}
/**
* wifidog 的gw_message 接口,信息提示页面
*/
function gw_message()
{
if (isset($_REQUEST["message"])) {
switch ($_REQUEST["message"]) {
case 'failed_validation':
//auth的stage为login时,被服务器返回AUTH_VALIDATION_FAILED时,来到该处处理
//认证失败,请重新认证
break;
case 'denied':
//auth的stage为login时,被服务器返回AUTH_DENIED时,来到该处处理
//认证被拒
break;
case 'activate':
//auth的stage为login时,被服务器返回AUTH_VALIDATION时,来到该处处理
//待激活
break;
default:
break;
}
}else{
//不回显任何信息
}
}
本文章由 http://www.wifidog.pro/2015/04/09/wifidog-php-2.html 整理编辑,转载请注明出处