WiFidog运行环境及及主要和认证服务器交互函数
0:WiFiDog运行环境
/wlan/portal/buildroot/etc # ps -w
\ PID USER VSZ STAT COMMAND
1 root 868 S init
2 root 0 SW< [kthreadd]
3 root 0 SW< [ksoftirqd/0]
4 root 0 SW< [events/0]
5 root 0 SW< [khelper]
6 root 0 SW< [async/mgr]
7 root 0 SW< [kblockd/0]
8 root 0 SW [pdflush]
9 root 0 SW [pdflush]
10 root 0 SW< [kswapd0]
11 root 0 SW< [crypto/0]
32 root 0 SW< [mtdblockd]
37 root 0 SWN [jffs2_gcd_mtd3]
564 root 864 S /usr/sbin/telnetd
566 root 864 S /usr/sbin/httpd -h /usr/www/
568 root 888 R -sh
881 nobody 1004 S dnsmasq
2191 root 868 R ps -w
2340 root 876 S udhcpd -S /etc/udhcpd.conf
3877 root 884 S udhcpc -i eth0 -p /var/run/udhcpc_wan.pid -s /etc/udhcpc.script
3892 root 1788 S wifidog -c /etc/wifidog.conf
4059 root 1788 S wifidog -c /etc/wifidog.conf
4060 root 1788 S wifidog -c /etc/wifidog.conf
4061 root 1788 S wifidog -c /etc/wifidog.conf
4062 root 1788 S wifidog -c /etc/wifidog.conf
/etc # ifconfig
ath0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0B:6B:B4:01:63
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1036165 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:902768 errors:0 dropped:181 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:173265983 (165.2 MiB) TX bytes:472405245 (450.5 MiB)
br0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0B:6B:B4:01:63
inet addr:192.168.100.10 Bcast:192.168.100.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1038127 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:895866 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:136852412 (130.5 MiB) TX bytes:451119780 (430.2 MiB)
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:03:7F:FF:FF:FF
inet addr:192.168.0.143 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:100545 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:83617 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:94237206 (89.8 MiB) TX bytes:9617979 (9.1 MiB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:50 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:50 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:5181 (5.0 KiB) TX bytes:5181 (5.0 KiB)
wifi1 Link encap:UNSPEC HWaddr 00-0B-6B-B4-01-63-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:2682769 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:3642860 errors:8464 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:511
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
Interrupt:64 Memory:b0000000-b0020000
/etc # brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
br0 8000.000b6bb40163 no ath0
/etc #
/etc # route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.100.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 br0
192.168.0.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
default 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
/etc # iptables -t nat -L
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
MASQUERADE all -- anywhere anywhere
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
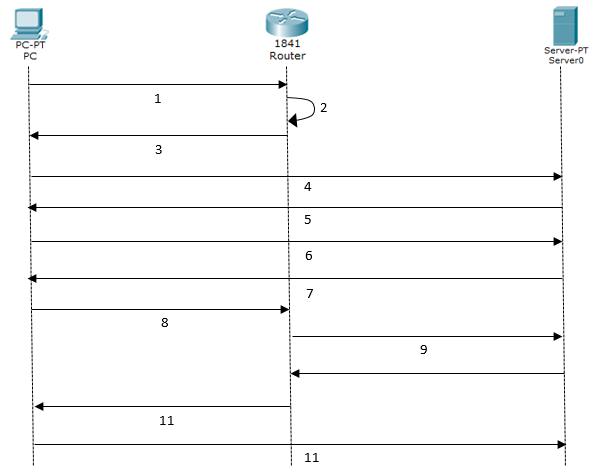
1: 用户,WiFiDog,Authpuppy交互过程
具体细节部分可以参考:http://dev.wifidog.org/wiki/doc/developer/FlowDiagram
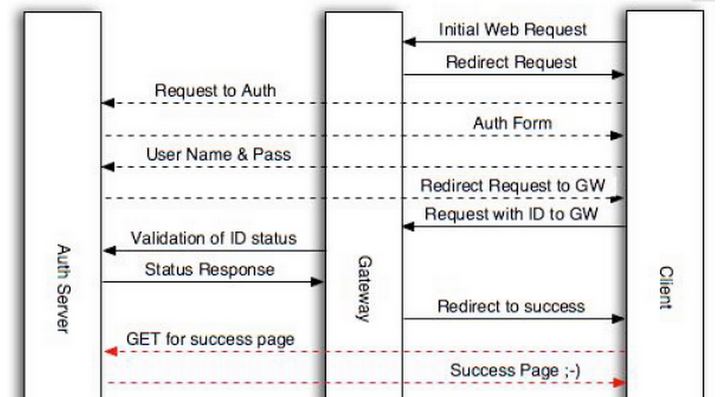
2:wifidog与authpuppy交互数据包
1) 当用户首次访问一个网址的时候:wifidog会将用户的请求重定义到登陆认证界面:
http://192.168.0.142:80/authpuppy/web/login/?gw_address=192.168.100.10&gw_port=2060&gw_id=123456789&mac=90:7a:28:01:20:26&url=www.baidu.com
2) authpuppy就回复一个包给运行wifidog的路由器的用户客户端浏览器,浏览器重定向到路由器:
http://GatewayIP:GatewayPort/wifidog/auth?token=[auth token]
3) 路由器与authpuppy之间的登陆认证数据:
http://192.168.0.142:80/authpuppy/web/auth/?stage=login&ip=192.168.100.11&mac=90:7a:28:01:20:26&token=9941ed0bc138c12c6edc4b1ed8358bd4516b86f2&incoming=0&outgoing=0&gw_id=123456789
4) authpuppy 回复一个auth code给路由器,表明token 正确与否
5) 路由器收到auth code:1,重定向浏览器:
http://192.168.0.142/portal/?gw_id=123456789
wifidog的路由器更新traffic counters到authpuppy
http://192.168.0.142:80/authpuppy/web/auth/?stage=counters&ip=192.168.100.11&mac=90:7a:28:01:20:26&token=9941ed0bc138c12c6edc4b1ed8358bd4516b86f2&incoming=1161884&outgoing=81646&gw_id=123456789
3:wifidog代码主要函数执行顺序
http_send_redirect_to_auth()函数是WiFidog路由器发送数据给用户的接口。
流程1:httpdGetConnection()-->thread_httpd()-->httpdReadRequest()-->httpdProcessRequest()-->http_callback_404()-->http_send_redirect_to_auth()
流程2:httpdGetConnection()-->thread_httpd()-->httpdReadRequest()-->httpdProcessRequest()-->http_callback_auth-->authenticate_client()-->
auth_server_request(&auth_response, REQUEST_TYPE_LOGIN, r->clientAddr, mac, token, 0, 0)-->fw_allow()-->iptables_fw_access()-->iptables_do_command()--->http_send_redirect_to_auth(r, urlFragment, "Redirect to portal");
本文章由 http://www.wifidog.pro/2014/12/16/WiFidog%E8%BF%90%E8%A1%8C%E7%8E%AF%E5%A2%83.html 整理编辑,转载请注明出处