wifidog 源码初分析(2)
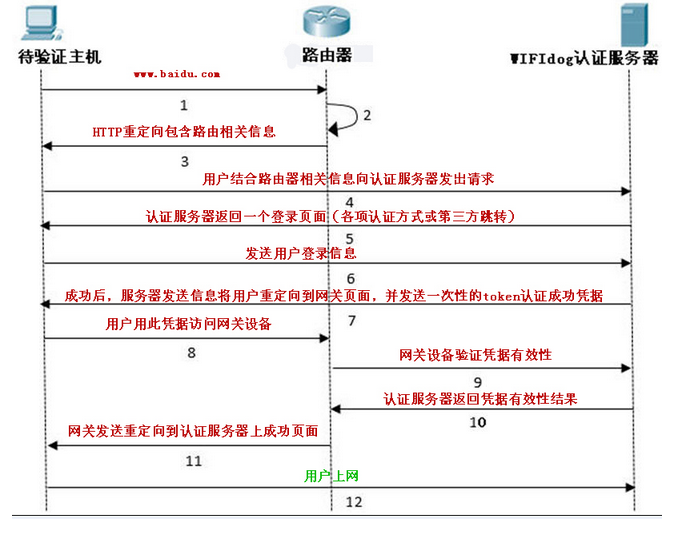
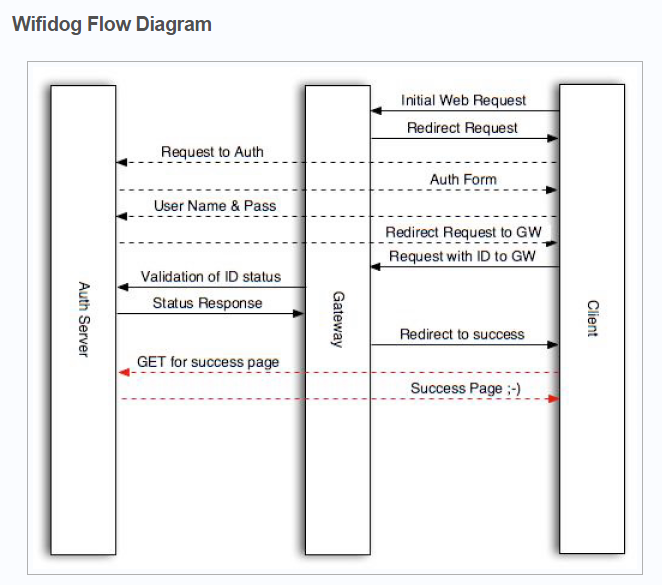
上一篇分析了接入设备的首次浏览器访问请求如何通过 防火墙过滤规则 重定向到 wifidog 的 HTTP 服务中,本篇主要分析了 wifidog 在接收到 接入设备的 HTTP 访问请求后,如何将此 HTTP 请求重定向到 认证服务器(auth-server) 上。
通过上面的防火墙规则,会将通过上面的防火墙规则,会将HTTP请求的外部IP地址和端口通过NAT方式重定向至本地wifidog内嵌HTTP服务器的地址和端口上,并由内嵌HTTP服务器进行服务,而内嵌HTTP服务器的路径和回调处理如下:
if ((webserver = httpdCreate(config->gw_address, config->gw_port)) == NULL) {
debug(LOG_ERR, "Could not create web server: %s", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
debug(LOG_DEBUG, "Assigning callbacks to web server");
httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/", "wifidog", 0, NULL, http_callback_wifidog);
httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "", 0, NULL, http_callback_wifidog);
httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "about", 0, NULL, http_callback_about);
httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "status", 0, NULL, http_callback_status);
httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "auth", 0, NULL, http_callback_auth);
httpdAddC404Content(webserver, http_callback_404);
客户端首次访问时回调客户端首次访问时回调http_callback_404函数,在该函数中根据获取的客户端信息来配置重定向的URL fragment,如下:
void
http_callback_404(httpd *webserver, request *r)
{
char tmp_url[MAX_BUF],
*url,
*mac;
s_config *config = config_get_config();
t_auth_serv *auth_server = get_auth_server();
memset(tmp_url, 0, sizeof(tmp_url));
/*
* XXX Note the code below assumes that the client's request is a plain
* http request to a standard port. At any rate, this handler is called only
* if the internet/auth server is down so it's not a huge loss, but still.
*/ /* 用户需要访问的URL */
snprintf(tmp_url, (sizeof(tmp_url) - 1), "http://%s%s%s%s",
r->request.host,
r->request.path,
r->request.query[0] ? "?" : "",
r->request.query);
url = httpdUrlEncode(tmp_url);
if (!is_online()) {
/* 路由器都接入不到 internet */
char * buf;
send_http_page(r, "Uh oh! Internet access unavailable!", buf);
free(buf);
}
else if (!is_auth_online()) {
/* auth server 挂起 */
char * buf;
send_http_page(r, "Uh oh! Login screen unavailable!", buf);
free(buf);
}
else {
/* 配置重定向到 auth server 的 url 参数 */
char *urlFragment;
if (!(mac = arp_get(r->clientAddr))) {
/* We could not get their MAC address */
debug(LOG_INFO, "Failed to retrieve MAC address for ip %s, so not putting in the login request", r->clientAddr);
safe_asprintf(&urlFragment, "%sgw_address=%s&gw_port=%d&gw_id=%s&url=%s",
auth_server->authserv_login_script_path_fragment,
config->gw_address,
config->gw_port,
config->gw_id,
url);
} else {
debug(LOG_INFO, "Got client MAC address for ip %s: %s", r->clientAddr, mac);
safe_asprintf(&urlFragment, "%sgw_address=%s&gw_port=%d&gw_id=%s&mac=%s&url=%s",
auth_server->authserv_login_script_path_fragment,
config->gw_address,
config->gw_port,
config->gw_id,
mac,
url);
}
/* 调用该函数将用户请求重定向到 auth server 的登录页面 */
http_send_redirect_to_auth(r, urlFragment, "Redirect to login page");
free(urlFragment);
}
free(url);
}
上面代码基本不用解释,具体重定向至auth server的消息在下面的 http_send_redirect_to_auth 函数中实现:
void http_send_redirect_to_auth(request *r, char *urlFragment, char *text)
{
char *protocol = NULL;
int port = 80;
t_auth_serv *auth_server = get_auth_server();
if (auth_server->authserv_use_ssl) {
protocol = "https";
port = auth_server->authserv_ssl_port;
} else {
protocol = "http";
port = auth_server->authserv_http_port;
}
char *url = NULL;
safe_asprintf(&url, "%s://%s:%d%s%s",
protocol,
auth_server->authserv_hostname,
port,
auth_server->authserv_path,
urlFragment
);
http_send_redirect(r, url, text);
free(url);
}
具体的重定向URL给个实例:
POST /login/?gw_address=192.168.1.1&gw_port=2060&gw_id=default&mac=44:94:fc:ef:28:40&url=http%3A//www.baidu.com/ HTTP/1.1
可以看到这里有这几个参数信息:
gw_address,路由器的LAN地址
gw_port:为wifidog的监听端口
gw_id:路由器的标识名
mac:客户端设备的MAC地址
url:为客户端访问的原URL(以便于重定向)
转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 、作者信息和本声明。否则将追究法律责任。http://quietmadman.blog.51cto.com/3269500/1384761
本文章由 http://www.wifidog.pro/2015/01/23/wifidog%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90-2.html 整理编辑,转载请注明出处